Fiberglass Truck Body: The Modern Solution for Commercial Fleets pickup.truckstrend.com
In the ever-evolving landscape of commercial transportation, businesses are constantly seeking innovative solutions to enhance efficiency, reduce operating costs, and extend the lifespan of their assets. Among the most significant advancements in truck body manufacturing is the widespread adoption of fiberglass. Far from being a mere alternative, the fiberglass truck body has emerged as a superior choice, offering a compelling blend of lightweight strength, unparalleled durability, and remarkable versatility. This comprehensive guide will delve into every aspect of fiberglass truck bodies, from their fundamental composition and myriad benefits to practical considerations for purchase, maintenance, and long-term performance.
What Exactly is a Fiberglass Truck Body?
Fiberglass Truck Body: The Modern Solution for Commercial Fleets
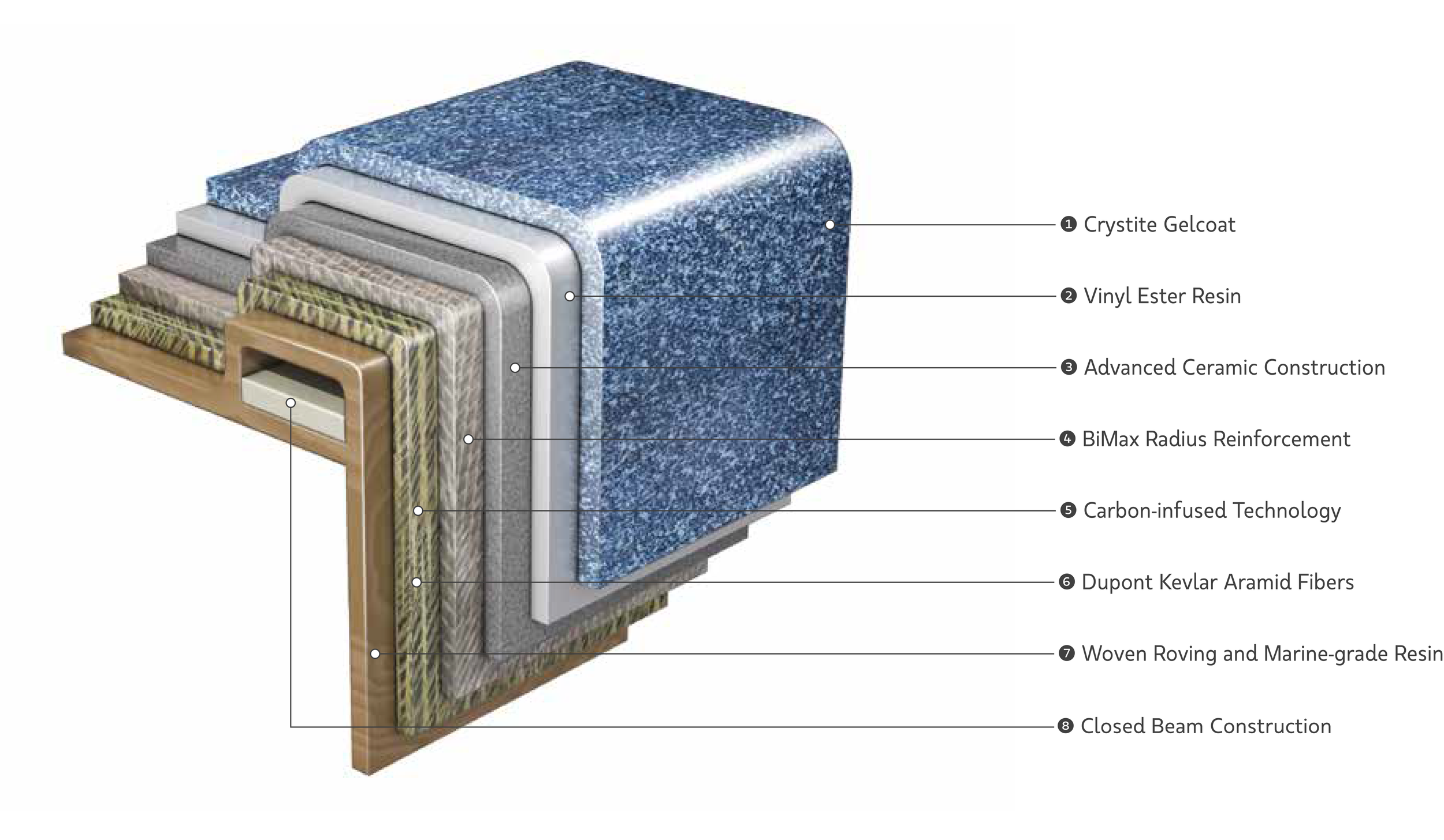
At its core, a fiberglass truck body is a composite structure crafted from a matrix of plastic resin reinforced with fine fibers of glass. This material, often referred to as Glass Reinforced Plastic (GRP) or Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP), is engineered to be incredibly strong yet remarkably light. The manufacturing process typically involves laying glass fibers (in various forms like mats or woven fabrics) into a mold and saturating them with a liquid thermosetting resin (such as polyester or vinyl ester). Once cured, this combination forms a rigid, monolithic structure that boasts an impressive strength-to-weight ratio, making it an ideal material for vehicle bodies.
Unlike traditional materials like steel or aluminum, fiberglass offers a unique combination of properties that cater specifically to the demands of modern commercial fleets, including superior resistance to corrosion, excellent thermal insulation, and exceptional design flexibility.
The Unrivaled Benefits of Fiberglass Truck Bodies
The growing popularity of fiberglass truck bodies is not a trend but a testament to their inherent advantages. These benefits translate directly into tangible savings and improved operational efficiency for businesses.
1. Lightweight Advantage: Fuel Efficiency & Increased Payload
One of the most compelling reasons to choose fiberglass is its significantly lighter weight compared to steel or even aluminum. A lighter truck body directly impacts fuel consumption, leading to substantial savings over the vehicle’s lifespan. Furthermore, the reduced tare weight allows for a higher payload capacity within legal Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) limits. This means businesses can transport more goods per trip, reducing the number of trips required and further cutting down on fuel and labor costs.
2. Superior Corrosion Resistance
Unlike steel, fiberglass does not rust or corrode. This makes it an ideal material for trucks operating in harsh weather conditions, coastal areas, or environments where exposure to road salt, chemicals, or moisture is common. The inherent resistance to environmental degradation ensures a longer aesthetic and structural life for the truck body, significantly reducing maintenance costs associated with rust prevention and repair.

3. Exceptional Durability and Longevity
Despite its lightweight nature, fiberglass is incredibly durable. It exhibits excellent impact resistance, often absorbing energy from minor collisions or impacts without denting or deforming like metal. Its flexible nature allows it to withstand vibrations and stresses without cracking, contributing to a longer service life. A well-maintained fiberglass body can outlast the truck chassis itself, making it a sound long-term investment.
4. Excellent Thermal Insulation Properties
Fiberglass naturally possesses good thermal insulation properties. This is a significant advantage for refrigerated truck bodies or those transporting temperature-sensitive goods, as it helps maintain consistent internal temperatures, reducing the energy required for refrigeration units. For dry freight, it can also offer a degree of protection against extreme external temperatures, safeguarding cargo.
5. Design Flexibility and Customization

The molding process used to create fiberglass bodies allows for immense design flexibility. Manufacturers can create complex shapes, integrated compartments, aerodynamic features, and custom configurations that would be difficult or costly to achieve with metal fabrication. This enables businesses to tailor truck bodies precisely to their specific operational needs, enhancing functionality and aesthetics.
6. Repairability and Reduced Maintenance
While fiberglass is durable, accidents can happen. Fortunately, fiberglass bodies are highly repairable. Damages, from minor cracks to significant structural breaches, can often be patched and restored to their original strength and appearance by skilled technicians. This ease of repair reduces downtime and extends the body’s life. Beyond repairs, routine maintenance is minimal, primarily involving regular cleaning and waxing to protect the gel coat from UV degradation.
Applications and Types of Fiberglass Truck Bodies
Fiberglass truck bodies are incredibly versatile and can be found across a wide range of industries and applications.

- Service & Utility Bodies: These are perhaps the most common fiberglass applications, featuring integrated tool compartments, shelving, and specialized storage solutions for electricians, plumbers, construction workers, and field technicians. Their lightweight nature allows service vehicles to carry more tools and equipment without exceeding weight limits.
- Dry Freight Bodies: Standard box truck bodies for general cargo transport. Fiberglass versions offer improved fuel efficiency and corrosion resistance over traditional aluminum or steel.
- Refrigerated Truck Bodies: Designed with enhanced insulation, these bodies are critical for transporting perishable goods, pharmaceuticals, and other temperature-sensitive items, maintaining precise climate control.
- Specialty & Custom Builds: Fiberglass is ideal for highly specialized applications like mobile laboratories, emergency response vehicles, mobile clinics, mobile showrooms, and even food trucks, where custom shapes, specific internal layouts, and durable, easy-to-clean surfaces are essential.
Manufacturing processes vary, including:
- Hand Lay-up/Spray-up: Traditional methods offering flexibility for custom shapes.
- Resin Transfer Molding (RTM): Produces parts with excellent surface finish on both sides and higher consistency.
- Sheet Molding Compound (SMC): A high-volume composite manufacturing process for parts requiring high strength and surface finish.
Manufacturing Process: From Resin to Road-Ready
The creation of a fiberglass truck body is a meticulous process that combines material science with skilled craftsmanship. While specific techniques vary, the general steps include:
- Mold Preparation: A highly polished mold, typically made from a durable material, is prepared. A release agent is applied to ensure the finished product can be easily removed.
- Gel Coat Application: A protective outer layer called a gel coat is sprayed into the mold. This provides the body with its color, UV resistance, and a smooth, glossy finish.
- Fiberglass Lay-up: Layers of fiberglass reinforcement (mats, woven rovings, chopped strands) are placed into the mold.
- Resin Application: Liquid resin, mixed with a catalyst, is applied to saturate the fiberglass layers. This can be done by hand (hand lay-up), sprayed (spray-up), or injected under pressure (RTM). The resin bonds the fibers together and gives the structure its rigidity.
- Curing: The resin and fiberglass mixture is allowed to cure, either at room temperature or in a heated oven, causing the resin to harden and form a solid composite.
- Demolding & Finishing: Once cured, the body is removed from the mold. Edges are trimmed, and any necessary drilling or bonding of internal structures (e.g., shelving, bracing) is performed.
- Assembly & Integration: The finished fiberglass body is then mounted onto the truck chassis, and any additional components like doors, lights, and internal fittings are installed.
Maintenance, Repair, and Longevity of Fiberglass Truck Bodies
While fiberglass is low-maintenance, proper care ensures its maximum lifespan and appearance.
Routine Care
- Regular Cleaning: Wash the body with mild soap and water to remove dirt, grime, and environmental contaminants.
- Waxing: Apply a marine-grade wax or automotive wax with UV inhibitors every 6-12 months. This protects the gel coat from sun damage, maintains its shine, and makes cleaning easier.
- Inspection: Periodically inspect the body for any signs of damage, cracks, or delamination, especially after long trips or heavy use.
Repairing Fiberglass Bodies
- Minor Scratches/Chips: Small blemishes in the gel coat can often be wet-sanded and buffed out. Deeper chips might require a gel coat repair kit.
- Cracks: Minor surface cracks can be filled with a fiberglass repair paste or epoxy. For more significant cracks that penetrate the laminate, professional repair involving grinding, layering new fiberglass, and re-gelling is recommended.
- Major Structural Damage: In cases of severe impact, professional fiberglass repair specialists can restore the structural integrity using specialized techniques, often making the repair virtually invisible. The ability to repair fiberglass, unlike some other materials that might require panel replacement, is a significant advantage.
- Painting: Fiberglass bodies can be painted if a custom color or branding is desired. Proper surface preparation and suitable automotive or industrial paints are essential for a durable finish.
Key Considerations Before Investing in a Fiberglass Truck Body
Choosing the right truck body is a significant investment. Here are crucial factors to consider:
- Initial Cost vs. Long-Term ROI: Fiberglass bodies often have a higher upfront cost than basic steel alternatives. However, their long-term value comes from fuel savings, reduced maintenance (no rust!), increased payload, and extended lifespan. Calculate the total cost of ownership over the vehicle’s expected life.
- Specific Business Needs: What kind of cargo will you transport? What are your typical routes? Do you need insulation? Custom compartments? Your operational requirements will dictate the ideal body type and features.
- Payload Capacity & GVWR: Ensure the lightweight fiberglass body allows you to maximize your payload without exceeding the truck’s Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) or Gross Combined Weight Rating (GCWR) if pulling a trailer.
- Chassis Compatibility: Verify that the fiberglass body is compatible with your chosen truck chassis in terms of size, mounting points, and weight distribution.
- Manufacturer Reputation & Warranty: Choose a reputable manufacturer known for quality construction and strong customer support. A good warranty provides peace of mind.
- Local Repair Capabilities: While fiberglass is repairable, ensure there are qualified repair shops in your area should the need arise.
Fiberglass vs. Traditional Materials: A Comparative Look
To fully appreciate the advantages of fiberglass, it’s helpful to compare it against its common counterparts:
| Feature | Fiberglass Truck Body | Steel Truck Body | Aluminum Truck Body |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightest (Significant fuel savings, higher payload) | Heaviest (Lower fuel economy, reduced payload) | Lighter than steel, heavier than fiberglass (comparably) |
| Corrosion | Excellent resistance (No rust, ideal for harsh areas) | Poor (Rusts easily, requires frequent anti-corrosion work) | Good (Oxidizes, but typically not destructive rust) |
| Durability | Good impact absorption, flexible, resists dents | Very strong, high tensile strength, prone to denting/rust | Good strength-to-weight, can be brittle in impacts |
| Repairability | Highly repairable (Patches, blends seamlessly) | Can be welded, but rust often complicates repairs | Can be welded, but requires specialized aluminum welding |
| Thermal Insul. | Good natural insulation | Poor (Conducts heat easily) | Poor (Conducts heat easily) |
| Design Flex. | Excellent (Molding allows complex, aerodynamic shapes) | Limited (Fabrication involves cutting, welding, bending) | Moderate (Easier to fabricate than steel, but still limited) |
| Cost (Initial) | Higher than basic steel, comparable to high-end aluminum | Lowest initial cost for basic models | Higher than steel, often comparable to fiberglass |
| Maintenance | Low (Washing, waxing, no rust treatment) | High (Rust prevention, painting) | Moderate (Less rust than steel, but can corrode) |
Tips for Maximizing Your Fiberglass Truck Body’s Performance
- Proper Loading: Distribute weight evenly within the body to prevent localized stress and maintain vehicle stability. Adhere to the body’s and chassis’s weight limits.
- Regular Inspections: Routinely check for any signs of stress cracks, especially around mounting points, doors, and high-stress areas. Early detection can prevent minor issues from becoming major repairs.
- Prompt Repairs: Address any damage, no matter how small, as soon as possible. Even minor cracks can propagate if left unattended.
- UV Protection: Consistent waxing is crucial to protect the gel coat from the sun’s UV rays, which can cause fading and chalking over time.
- Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Use only mild, non-abrasive cleaners on your fiberglass body. Strong solvents or harsh chemicals can damage the gel coat.
Addressing Potential Challenges
While fiberglass truck bodies offer numerous advantages, it’s important to be aware of potential challenges and their solutions:
- Higher Initial Cost: As noted, fiberglass bodies often have a higher upfront investment. Solution: Focus on the long-term total cost of ownership (TCO). The savings in fuel, maintenance, and extended lifespan typically outweigh the initial premium.
- Impact Vulnerability: While resistant to dents, severe, sharp impacts can cause fiberglass to crack or shatter, unlike steel which might just bend. Solution: While unavoidable in some accidents, careful driving and proper loading reduce risk. For existing damage, the good news is fiberglass is highly repairable by skilled technicians.
- UV Degradation: Without proper care, the gel coat can chalk or fade over time due to UV exposure. Solution: Regular washing and, critically, consistent waxing with a UV-protective wax will maintain the body’s aesthetic appeal and extend its life.
- Specialized Repair: While repairable, fiberglass repair often requires specific knowledge and materials different from metalwork. Solution: Choose a manufacturer or dealer who can recommend qualified fiberglass repair specialists, or invest in training for your in-house maintenance team if your fleet is large enough.
Illustrative Price Guide for Fiberglass Truck Bodies
Please note that prices for fiberglass truck bodies vary significantly based on size, features, level of customization, manufacturer, and current market conditions. The table below provides illustrative price ranges for common types of fiberglass truck bodies to give you an idea of the investment involved. These are estimates and actual quotes will vary.
| Body Type | Size / Capacity | Estimated Price Range (USD) | Key Factors Affecting Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Service/Utility Body | Small (8-10 ft chassis) | $8,000 – $15,000 | Number/type of compartments, integrated ladder racks, lighting, interior finishing. |
| Medium (12-14 ft chassis) | $12,000 – $25,000 | ||
| Large (16-20 ft chassis) | $20,000 – $40,000+ | ||
| Dry Freight Body | 10 ft (Small box truck) | $10,000 – $18,000 | Interior lining, roll-up vs. swing doors, side doors, custom shelving. |
| 14 ft (Medium box truck) | $15,000 – $25,000 | ||
| 18-24 ft (Large box truck) | $20,000 – $40,000+ | ||
| Refrigerated Body | Small (10-14 ft chassis) | $25,000 – $50,000+ | Insulation thickness, refrigeration unit type, multiple compartments, internal finishes. |
| Medium (16-20 ft chassis) | $40,000 – $80,000+ | ||
| Large (22-26 ft chassis) | $60,000 – $120,000+ | ||
| Custom/Specialty | Varies (e.g., Mobile Clinic) | $50,000 – $200,000+ | Complexity of design, specialized equipment integration, interior build-out, certifications. |
Note: These prices typically do not include the truck chassis, installation costs, or any additional custom equipment/outfitting.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Fiberglass Truck Bodies
Q1: How durable are fiberglass truck bodies compared to steel or aluminum?
A1: Fiberglass is exceptionally durable. While steel is stronger in terms of tensile strength and aluminum is lighter, fiberglass offers a unique balance. It’s highly resistant to corrosion, impacts (it flexes rather than dents), and general wear and tear. It won’t rust, significantly extending its lifespan compared to steel.
Q2: Can fiberglass truck bodies be repaired if damaged?
A2: Absolutely. One of the major advantages of fiberglass is its repairability. Minor scratches, cracks, and even significant structural damage can often be patched, filled, and refinished by skilled technicians, restoring the body to its original strength and appearance.
Q3: Are fiberglass truck bodies more expensive than steel or aluminum?
A3: The initial purchase price of a fiberglass truck body can sometimes be higher than a basic steel body. However, when considering the total cost of ownership (TCO) over the vehicle’s lifespan, fiberglass often proves more cost-effective due to significant fuel savings, reduced maintenance (no rust!), and a longer operational life. They are often comparable to or less expensive than high-grade aluminum bodies.
Q4: Do fiberglass bodies really save on fuel costs?
A4: Yes. Fiberglass bodies are significantly lighter than steel bodies. This reduced weight directly translates to lower fuel consumption, especially over long distances or in stop-and-go urban driving. The savings can be substantial over the lifetime of the vehicle.
Q5: What is the typical lifespan of a fiberglass truck body?
A5: With proper maintenance and care, a fiberglass truck body can easily last 15-20 years or more, often outliving the chassis it’s mounted on. Its inherent resistance to rust and corrosion is a major factor in its longevity.
Q6: Do fiberglass bodies rust or corrode?
A6: No. Fiberglass (FRP) is a composite material that is inherently resistant to rust, corrosion, and most chemicals. This makes it an excellent choice for operations in harsh environments, coastal areas, or where de-icing salts are used.
Q7: Can I customize the interior of a fiberglass truck body?
A7: Yes, fiberglass offers excellent design flexibility. Interiors can be highly customized with shelving, drawers, specific compartments, lighting, and insulation to meet diverse operational needs, from mobile workshops to refrigerated units.
Conclusion
The fiberglass truck body represents a paradigm shift in commercial vehicle design, offering a compelling blend of lightweight efficiency, robust durability, and unparalleled versatility. By shedding unnecessary weight, resisting the ravages of corrosion, and providing a platform for highly customized solutions, fiberglass bodies empower businesses to operate more efficiently, reduce their environmental footprint, and enhance their bottom line. While the initial investment might seem higher, the long-term benefits in fuel savings, reduced maintenance, increased payload, and extended service life make fiberglass an intelligent and forward-thinking choice for any fleet manager or business owner looking to optimize their transport operations. Embracing fiberglass isn’t just about choosing a material; it’s about investing in a smarter, more sustainable future for your fleet.